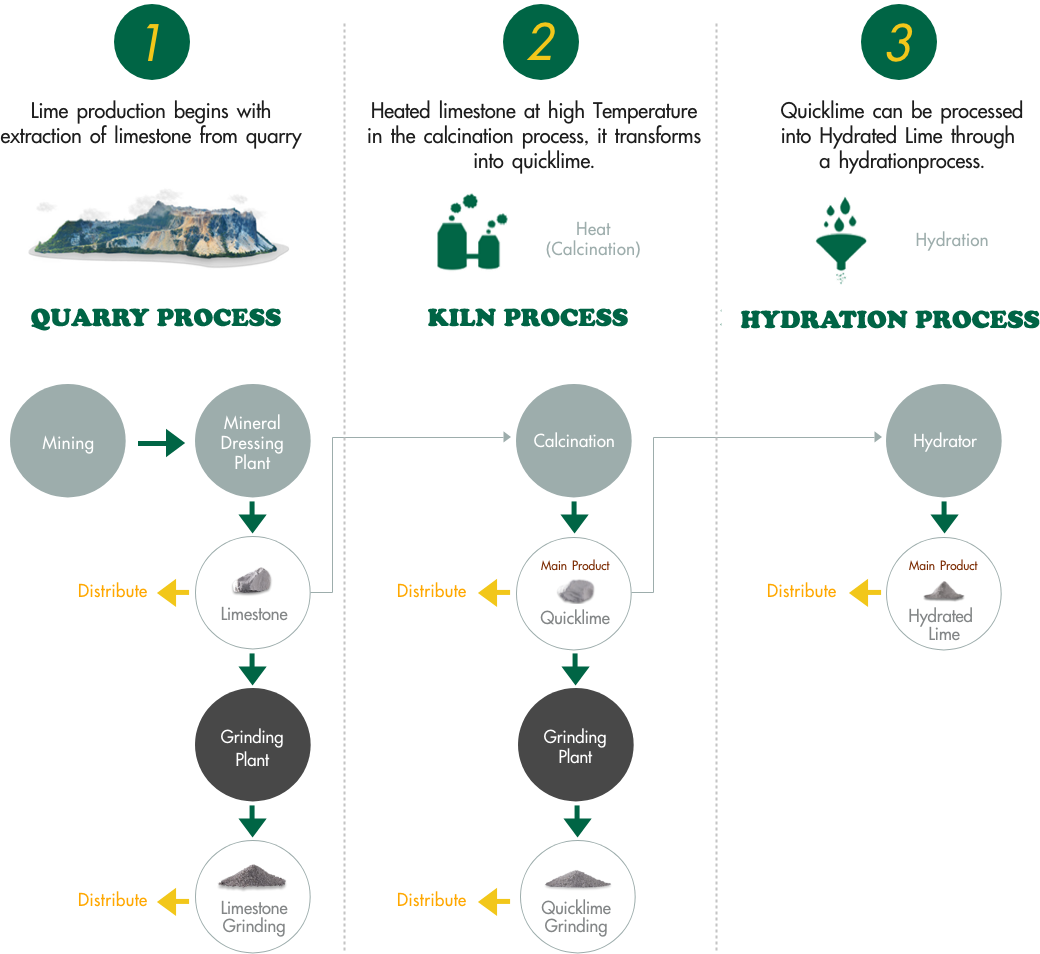
Step-1
lime production begins with extraction of limestone from quarry.Limestone is extracted from the rock either by blasting or mechanical excavation depending on the hardness of the rock.
Step-2
Heated limestone at high temperature in the calcination process , it transforms into quick lime.
Step-3
quicklime can be processed into Hydrated lime through a hydration process.
Hydrated Lime is defined as a process whereby approximately stoichiometric amounts of water and lime react to form a product, hydrate, which is a dry powder; i.e. it contains less than 1% free moisture and is handled as a powder. ... It is formed when quicklime or calcium oxide (CaO) comes into contact with water.
A method of producing a hydrated lime. The process hydrates quicklime in conjunction with standard means of hydrating lime.The resulting hydrated lime has highly reduced contents of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide. The hydrated lime has little to no remaining reactivity when placed in contact with water after the process. The hydrated lime can is with stoichiometric volumes of water as required to fully hydrate the quicklime and water mixture as well as with volumes beyond the calculated stoichiometry with some potential for remaining water left after the process without the potential for lime putty or a wet hydrate as the result.
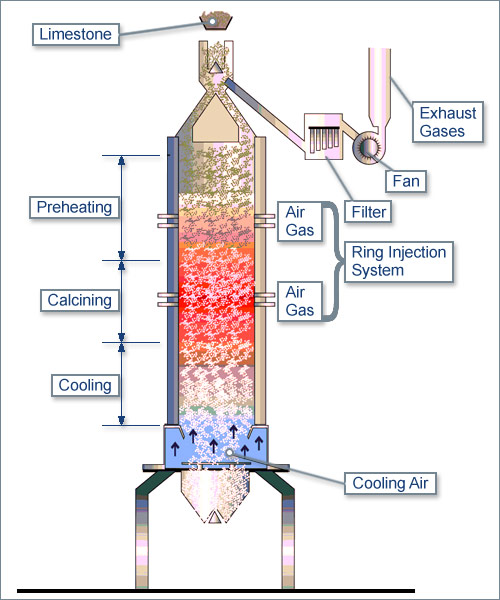
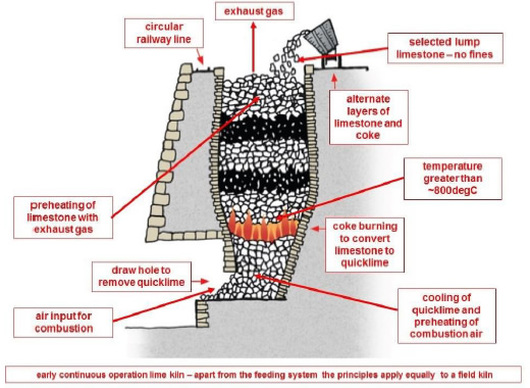
Lumps of limestone are heated to a temperature in excess of about 800oC, carbon dioxide is driven off and what remains is quicklime, calcium oxide. limestone decomposes into quicklime and carbon dioxide
CaCO3 --> CaO + CO2
By weight 100 --> 56 + 44
The process is called ‘calcination’. If calcination is carried out correctly the lumps of quicklime are
approximately the same size as the original lumps of limestone but much less dense, because of the
weight loss of 44% arising from the removal of carbon dioxide.
© 2020 R K Chemicals. All Rights Reserved | Design & Developed by Dheer Software Solutions